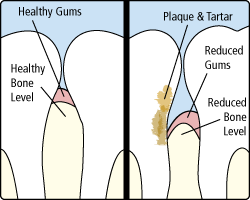
Periodontal disease, commonly called gum disease, refers to infection of the gums surrounding your teeth. Gum disease is one of the main reasons adults lose teeth. Because gum disease is generally not painful, many people remain unaware of their gum disease and its impact on their dental health. Your dentist will check for signs of periodontal disease by measuring the space between your teeth and gums when you have your routine exams. This is just one more reason why keeping up with routine dental exams is so important to maintaining a healthy smile.
Causes of Gum Disease
Plaque is a sticky form of bacteria that forms on the teeth. If plaque is not removed by flossing, brushing, and regular dental checkups, it will continue to build up. Gum disease is caused by this plague buildup, which creates toxins that can damage the gums. Periodontal disease creates small pockets that separate the gums from the teeth just below the gum line.
There are two states to periodontal disease:
- Gingivitis — This is the early stage when the gums become red, swollen, and bleed easily. Gingivitis is very treatable and can generally be eliminated by daily brushing and flossing.
- Periodontitis — Left unchecked gingivitis will advance into periodontitis. Periodontitis causes serious and irreversable damage to the gums and bone that support the teeth. Periodontitis can cause teeth to become loose, fall out, or require extraction by a dentist.
Gum Disease Risk Factors
Listed below are some lifestyle habits, events, and conditions that can increase your risk of gum disease:
- Smoking or using chewing tobacco
- Diabetes
- Certain types of medication such as steroids, anti-epilepsy drugs, cancer therapy drugs, calcium channel blockers, and oral contraceptives
- Bridges that no longer fit properly
- Crooked teeth
- Old fillings
- Pregnancy
Gum Disease Symptoms
Although gum disease often goes undiagnosed until a dentist examination, below are some symptoms that may indicate gum disease is present:
- Gums that bleed easily
- Red, swollen, tender gums
- Gums that have pulled away from the teeth
- Persistent bad breath or bad taste
- Pus between your teeth and gums
- Permanent teeth that are loose or separating
- Any change in the way your teeth fit together when you bite
- Any change in the fit of partial dentures
Gum Disease Treatment
Treatments for gum disease vary depending on how advanced the disease has become. Typical treatments include:
- Non-surgical treatments such as at-home periodontal trays, and scaling and root planing (deep cleaning)
- Periodontal surgery and laser gum surgery
- Dental implants
Gum Disease Prevention
Regular dental checkups and periodontal examinations are important for maintaining your health and the health of your smile. You don't have to lose teeth to periodontal disease, and by practicing good oral hygiene at home, you can significantly reduce your chances of ever getting gum disease. Remember to brush regularly, clean between your teeth, eat a balanced diet, and schedule regular dental visits to help keep your smile healthy.







